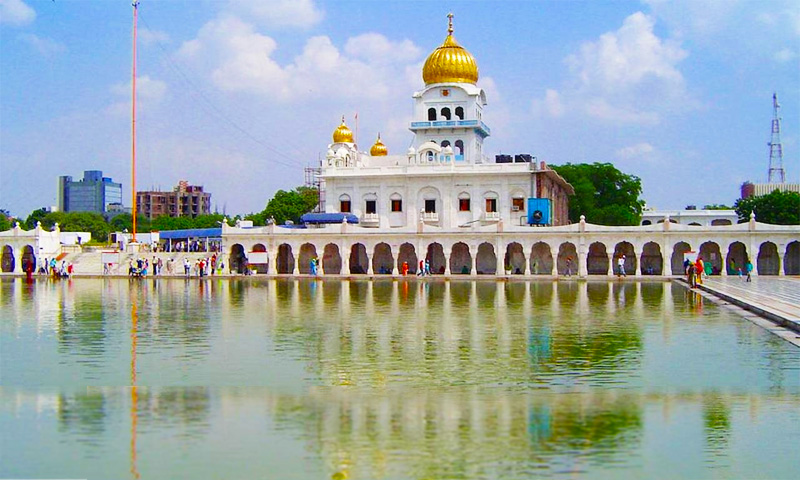
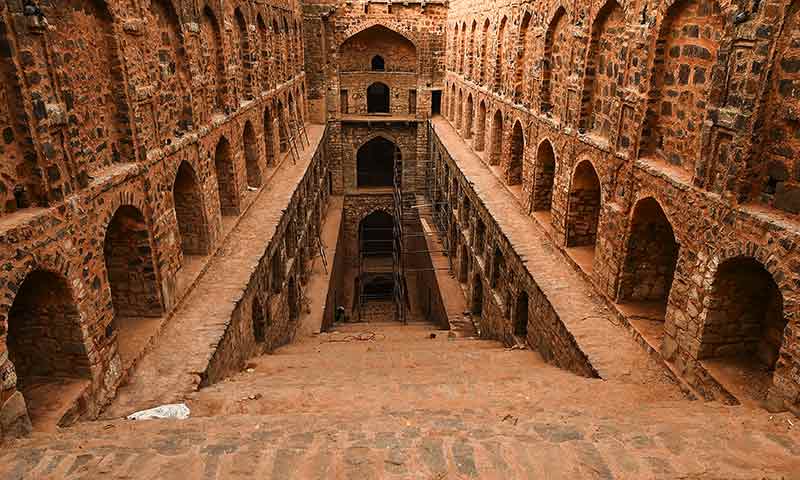
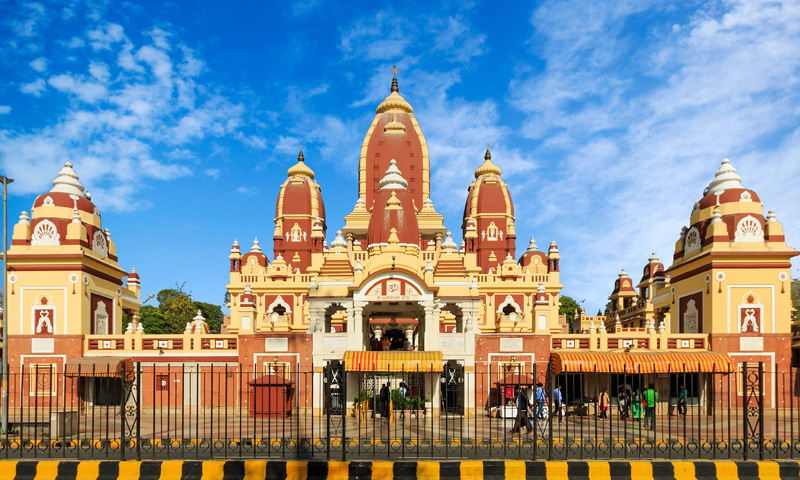
Jantar Mantar, Delhi
Online Tickets (ASI website):
Adults Indians (per person): ₹20/-
Foreigners (per person): ₹250/-
BIMSTEC, SAARC Countries (per person): ₹20/-
Offline Tickets (On-site Purchase):
Adults Indians (per person): ₹25/-
Foreigners (per person): ₹300/-
BIMSTEC, SAARC Countries (per person): ₹25/-
Entry is free for children below 15 years
Find Metro Route For Attraction
About Jantar Mantar
Jantar Mantar, located on Janpath in Delhi, India, is an astronomical observatory built in 1724 by Maharaja Sawai Jai Singh II of Jaipur during the Mughal period. It was designed to measure time, predict eclipses, track celestial bodies, and create astronomical tables. Spread over an area of approximately 1,500 square metres, this observatory showcases a blend of Hindu architectural principles and scientific innovation. Its highlights include the Samrat Yantra (large sundial) and the Jai Prakash Yantra, large geometric instruments designed for precise astronomical calculations. Jantar Mantar is an important site for both cultural tourism and historical research, providing insight into the scientific achievements of the 18th century in India.
Architecture of Jantar Mantar
The Jantar Mantar in Delhi exemplifies the architectural style of large-scale geometric construction, serving a functional and scientific purpose. Built in 1724 by Maharaja Sawai Jai Singh II, it reflects a fusion of Rajput and Mughal architectural influences, with an emphasis on accuracy and durability. The observatory's design was carefully planned according to astronomical principles, using angled planes, circular structures, and a graduated scale for celestial measurements. The structure is constructed of masonry, stone, and lime plaster, demonstrating the advanced construction techniques of the time. The observatory houses several large instruments:
- Samrat Yantra – the largest sundial that accurately measures time
- Jai Prakash Yantra – a hemispherical structure for observing sky positions
- Rama Yantra – a cylindrical instrument for measuring altitude and azimuth
- Mishra Yantra – for determining the exact time of noon at different locations
- The layout includes integrated small quadrants, scales, and observational platforms
The layout and orientation of each instrument were precisely calculated to track sky phenomena, showcasing a fusion of architectural art with scientific innovation.
Interesting facts about Jantar Mantar
- Constructed using stone, marble, and lime plaster to ensure stability and long-term precision.
- The Samrat Yantra sundial can measure time with an accuracy of up to two seconds
- Each instrument is aligned according to the cardinal directions and celestial coordinates.
- The observatory incorporates symbolic geometrical shapes reflecting Hindu cosmological concepts.
- Archaeological studies have revealed writings detailing the astronomical calculation methods used by Jai Singh II.
- Jantar Mantar represents an early example of combining architecture with empirical science for public and royal use.
How to reach Jantar Mantar
Jantar Mantar on Google Map
Nearby Places
Bus Stop
Cinema
College
Event Venue
Hospital
Hotel
Other
Railway Station
Restaurant & Bars
School
Jantar Mantar FAQs:
𝒜. Jantar Mantar is one of the most accurate pre-modern observatories in the world, and attests to eighteenth-century efforts to improve the understanding of planets and other cosmic ones.
𝒜. Jantar Mantar was built by Sawai Jai Singh II.
𝒜. It was built in the year 1724.
𝒜. Its elevation is 723 feet (220 m).
𝒜. "Jantar Mantar" literally means "instrument for measuring the harmony of heaven". It consists of 13 architectural astronomy instruments.
𝒜. It is located at Janpath, Delhi.
𝒜. Entry fee and timings information of the Jantar Mantar: INR 25 for Indians, INR 300 for Foreigners 6:00am to 6:00 pm. Everyday..
𝒜. You should visit Jantar Mantar during June, July, August months for best experience.
📅 Last update: 2026-01-26 || ✍ Author: Sandhya Chauhan
Meet Sandhya, exploring India with curiosity and wonder. She shares info and tips in simple language, inviting you to join the journey. She is graduated in tourism and writes about the places of India.
Explore other attractions nearby
🛑Note: Information is for reference purpose only.