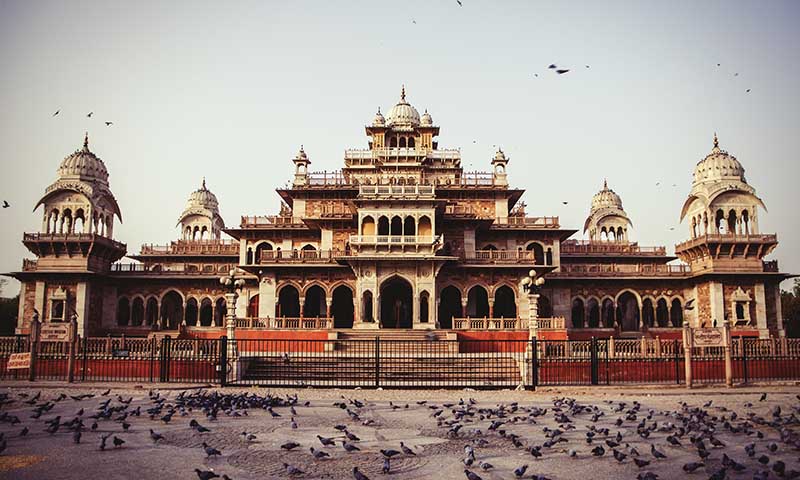
Jantar Mantar, Jaipur
Find Metro Route For Attraction
About Jantar Mantar
The Jantar Mantar in Jaipur is a remarkable astronomical observatory dating back to the early 18th century, commissioned by Jaipur's founder, Rajput king Sawai Jai Singh II. Completed in 1734, this UNESCO World Heritage Site exemplifies the scientific and cultural aspirations of its time and served as a center for observing the skies and calculating time. Spread over approximately 18,700m² (about 4.6 acres), Jantar Mantar houses a magnificent collection of stone and marble instruments, showcasing a blend of Hindu, Islamic, Persian and European influences.Its layout and large sundial reflect the advanced astronomical knowledge possessed by the Jaipur court.
Architecture of Jantar Mantar
Jantar Mantar's architectural style is unique and functional, based on scientific and practical thinking rather than traditional ornamental design. As an astronomical observatory, its structures are large instruments made of local stone, marble, bronze, and brick, designed in precise geometric shapes to measure time, celestial coordinates, the direction of the Sun, and the positions of the planets. Designed to be visible to the naked eye, this space combines technical design with cosmological symbols, based on the principles of Vastu Shastra and scientific cosmology.
It was built between 1728–1734 during the reign of Maharaja Sawai Jai Singh II in the state of Amber (later Jaipur). This period marked the Scientific Renaissance, where new thinking in astronomy, mathematics, and architecture combined to create one of India's most distinctive observatories.
- Major structures inside the monument:
- Samrat Yantra – World’s largest stone sundial
- Laghu Samrat Yantra – Smaller sundial variant
- Jai Prakash Yantra – Inverted bowl instrument
- Ram Yantra – Paired circular instruments
- Chakra Yantra – Ring instrument for coordinates
- Nadivalaya – Two circular plate hemispheres
- Digamsa Yantra – Azimuth measurement device
Interesting facts about Jantar Mantar
- The Samrat Yantra sundial at Jantar Mantar can measure local time with an accuracy of up to two seconds.
- Jantar Mantar contains 19 astronomical instruments, each carefully calibrated for specific celestial measurements.
- The monument embodies a fusion of architectural influences including Hindu, Islamic, Persian and early European scientific design.
- Instruments were built with local stone and marble with fine astronomical graduation marked in marble inlays.
- The layout is aligned with the cardinal directions, reflecting traditional Indian architectural principles (Vastu) to enhance visual accuracy.
- Jai Singh II built five Jantar Mantar observatories across India; Jaipur’s is the most complete and largest.
How to reach Jantar Mantar
Jantar Mantar on Google Map
Nearby Places
Bus Stop
Hotel
Other
Railway Station
Restaurant & Bars
School
Shopping Place
Jantar Mantar FAQs:
𝒜. It is located at Gangori Bazaar, J.D.A. Market, Pink City, Jaipur, Jaipur.
𝒜. Entry fee and timings information of the Jantar Mantar: Jantar Mantar is open from 09:00 am to 04:30 pm all days in week, The entry fee for Indian Rs 50 and for foreigner Rs 200..
𝒜. You should visit Jantar Mantar during January, February months for best experience.
📅 Last update: 2026-01-26 || ✍ Author: Sandhya Chauhan
Meet Sandhya, exploring India with curiosity and wonder. She shares info and tips in simple language, inviting you to join the journey. She is graduated in tourism and writes about the places of India.
Explore other attractions nearby
🛑Note: Information is for reference purpose only.